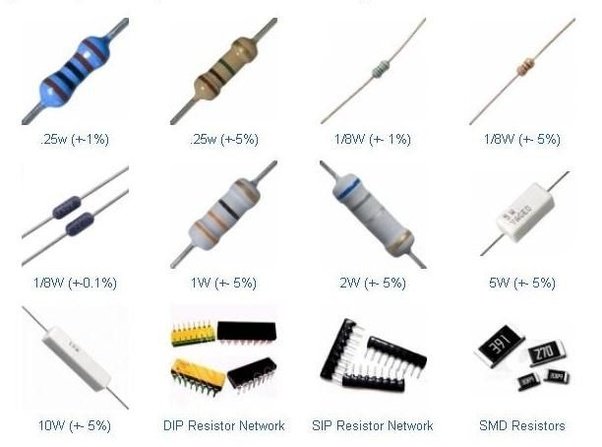
RESISTORS
Briefly, the difficulty shown in electrical current is called RESISTANCE, indicated by the letter "R" or "r" and its unit is ohms (Ω).
FUNCTIONS OF RESISTORS
I. Keep the circuit current constant by limiting
II. Use as a voltage divider in the circuit
III. High-current protection of sensitive circuit elements
IV. Use as load in the circuit
V. Heat energy generation
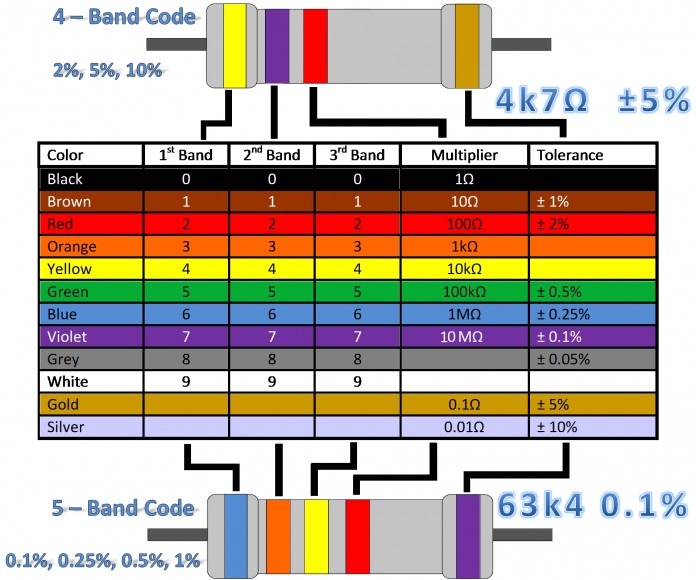
Carbon Resistances are obtained by heating melted carbon and resins in powder form. The amount of carbon in the mixture determines the value of the resistance. They are produced in sizes ranging from 1⁄4 - 1/2 - 1 - 2 - 3 watts and 1ohm to 22 M according to their size. Specifies values from colored lines.
Stone Resistors; These are the resistances that are made from the materials such as chrome-nickel, nickel-silver, tungsten, manganese, which are made of materials such as porcelain, bakelite, asbestos. Stone resistors produced using high-resistance metals are high-power elements that can be passed over high current.
SMD (Surface Montage Device); It is used especially in serial production cards because it requires very little space and enables the production of new generation typesetting machines very quickly. 0201; 0402; 0604; 0805; 1206; There are kinds of 2010 cases. The numbers on the resistor indicate their value. It usually carries a 3 or 4 digit number. The first digits represent the digit, the last digit multiplier, and the letter R indicates a comma. For example, 2200 = 220 × 10 ^ 0 = 220Ω, 102 = 10 × 10 ^ 2 = 1KΩ, 1R2 = 1.2Ω
Resistance Color Code Reading;